Bonomi Acciai è lieta di annunciare la propria partecipazione a EUROGUSS…
Induction Hardening Treatment
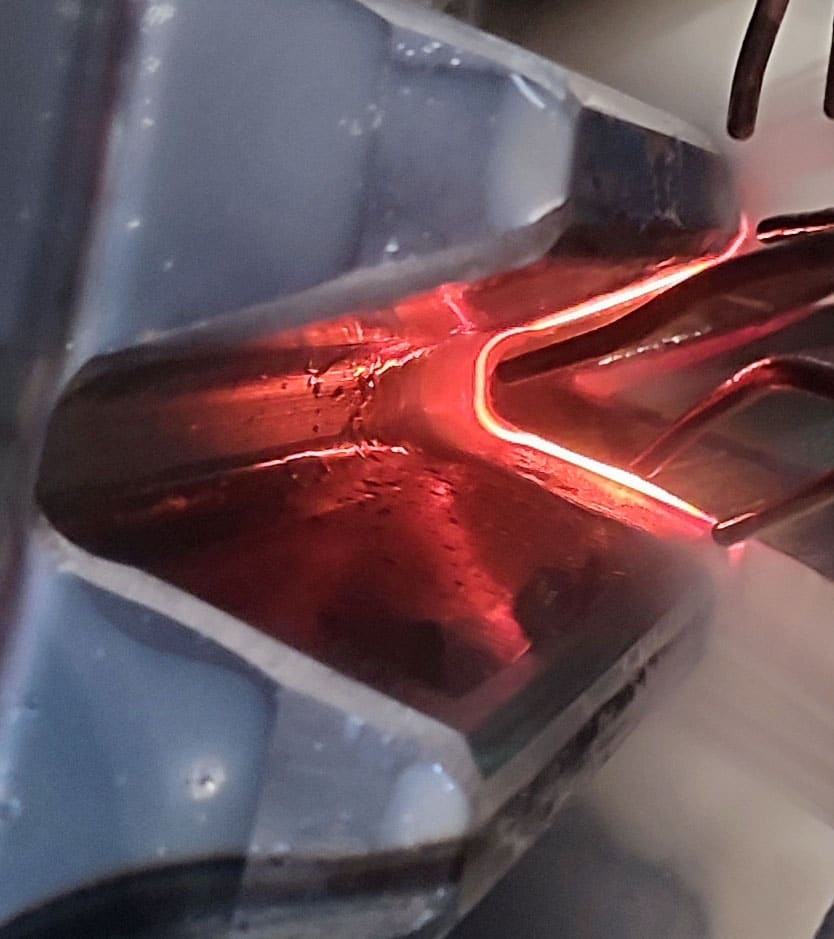
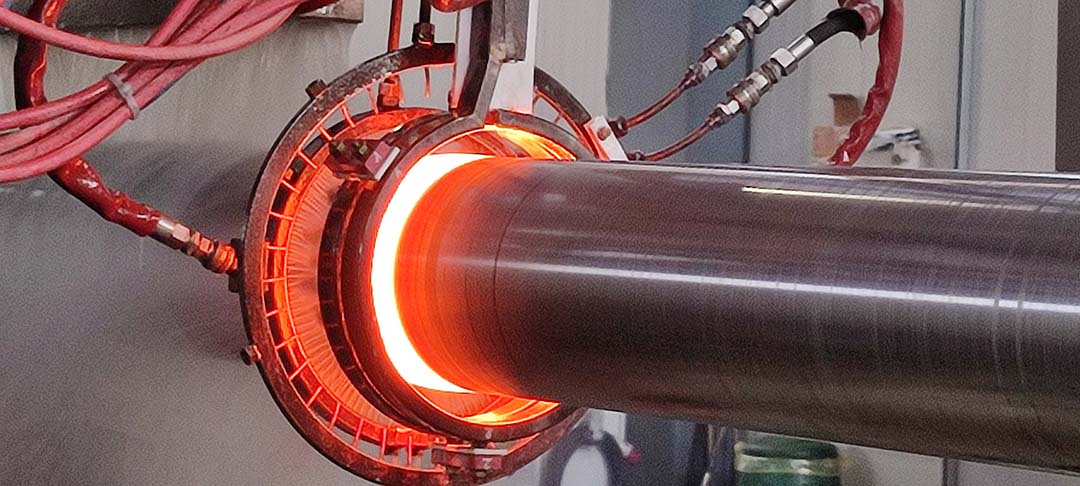
Induction hardening is a surface heat treatment process designed to improve the wear resistance and fatigue strength of components subject to high stress or friction.
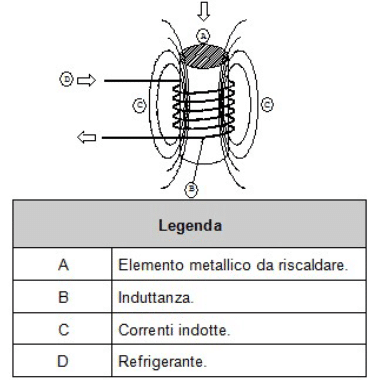
The process involves rapid heating—caused by Joule effect from induced currents—of a metallic body (a good electrical conductor) placed inside a variable electromagnetic field generated by an inductor.
Heating occurs without physical contact: the induced electrical currents heat the material to austenitic temperatures in a matter of seconds, allowing precise control over the desired case depth.
This is followed by a quenching phase—achieved through immersion or spray nozzles—using different quenching media (air blast, water, or polymer solutions), depending on the steel grade (including quenched-and-tempered steels) and performance requirements.
To avoid overheating during operation, the induction coil is typically cooled by internal circulation of demineralized water.
In industrial applications, heating is achieved using:
-
Low-frequency generators (< 2 kHz)
-
Medium-frequency generators (2 ÷ 30 kHz)
-
High-frequency generators (> 150 kHz)
The depth of the heated layer is inversely proportional to the frequency: low frequencies produce deeper hardening, while high frequencies affect only a few millimetres.
Advantages of Induction Hardening
This treatment significantly increases surface hardness and wear resistance, extending the service life of components.
Compared to traditional furnace-based processes, the main benefits include:
-
Flexibility: selectively hardens specific areas of any geometry without altering the core.
-
Speed: heating and cooling occur within seconds.
-
In-line integration: one of the few heat treatments that can be implemented directly on a production line.
Applications of Induction Hardening
The process is widely used in sectors such as automotive, rail, marine, energy, aerospace, and heavy mechanics.
Examples of localized induction hardening include:
-
Rollers, cylinders, columns, shafts
-
Power transmission components (gears, pinions, racks, slewing rings)
-
Wheels, sheaves, capstans, pulleys
-
Crossbeams, guides, blades
-
Dies and molds
Conclusion
Induction hardening makes it possible to obtain hard, wear-resistant surfaces while preserving the toughness of the core. A fast, precise, and localized treatment—ideal for enhancing the performance and longevity of mechanical components.
Bonomi Acciai, official representatives in Italy of Swiss Steel Group, support engineers in selecting the most suitable steels and thermal treatments for every specific application.
Would you like to learn more?